The Imperative for a Sustainable Food System
The global food system stands at a critical juncture. Traditional agriculture, while feeding billions, is a major contributor to environmental degradation, accounting for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, and deforestation. The challenge is immense: how do we feed a growing global population—projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050—without exhausting the planet’s finite resources? The answer lies not in expanding the old model, but in pioneering a new one.
This is where Infarmight, a leader in smart farming technology, enters the picture. By leveraging advanced vertical farming, AI-driven climate control, and closed-loop systems, Infarmight is not just optimizing crop yield; it is fundamentally redefining the environmental footprint of food production. Their mission is clear: to create a resilient, localized, and profoundly sustainable food network. This post delves into the core environmental benefits that position Infarmight as a cornerstone of a greener tomorrow.
1. The Water Revolution: Conservation in a Closed-Loop System
Water scarcity is arguably the most pressing environmental challenge facing agriculture. Conventional farming is a notorious water guzzler, with irrigation accounting for approximately 70% of the world’s freshwater withdrawals. Infarmight’s technology offers a radical solution to this problem through its sophisticated hydroponic and aeroponic systems.
1.1. Efficiency by Design
Infarmight’s farms operate on a closed-loop water recycling system. Unlike open-field irrigation where water is lost to evaporation, runoff, and percolation, their systems capture, filter, and reuse water that is not absorbed by the plants. This continuous recycling dramatically reduces the need for fresh water input.
The precision of their nutrient delivery system, managed by AI, ensures that plants receive the exact amount of water and nutrients they need, minimizing waste. This level of control is impossible in traditional settings. The result is a staggering reduction in water usage.
Infarmight’s vertical farms use up to 95% less water compared to conventional farming methods for the same crops. This massive saving is not just an operational efficiency; it is a critical environmental contribution in regions facing drought and water stress.
1.2. Protecting Waterways
Beyond sheer volume reduction, Infarmight’s approach protects natural water bodies. Traditional agriculture often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which are carried by runoff into rivers, lakes, and oceans. This nutrient pollution, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus, leads to eutrophication, creating “dead zones” where aquatic life cannot survive.
Because Infarmight’s systems are entirely contained and chemical-free (a point we will explore further), there is virtually no agricultural runoff. The nutrients are precisely managed within the closed system, preventing them from ever entering the external environment. This single factor represents a profound ecological benefit for freshwater and marine ecosystems.
2. Land Use and the Power of Verticality
The expansion of agriculture is the primary driver of deforestation and habitat loss globally. To meet food demand, forests are cleared, wetlands are drained, and biodiversity is lost. Infarmight’s vertical farming model directly addresses this issue by decoupling food production from vast tracts of arable land.
2.1. Unlocking Urban Spaces
Infarmight’s modular, stackable farms can be installed in existing urban infrastructure—warehouses, abandoned buildings, or even shipping containers. This vertical stacking allows for the cultivation of massive quantities of food on a tiny fraction of the land required by conventional farms.
Consider the concept of “farm-to-table” distance. By locating farms within or immediately adjacent to population centers, Infarmight eliminates the need for large, remote agricultural lands. This not only preserves natural habitats but also transforms underutilized urban spaces into productive, green assets.
2.2. Restoring Ecosystems
The shift to vertical farming frees up conventional farmland, offering an opportunity for land sparing and ecological restoration. As the pressure to maximize yield on existing land decreases, marginal or degraded farmlands can be allowed to revert to their natural state, fostering biodiversity and sequestering carbon. Infarmight’s technology provides a viable path to increasing food security while simultaneously reducing the human footprint on wild ecosystems.
3. Decarbonizing the Supply Chain: Energy and Logistics
The environmental impact of food extends far beyond the farm gate. The energy required to grow, harvest, process, package, and transport food—often across continents—contributes significantly to global carbon emissions. Infarmight tackles this challenge through two key strategies: localization and energy optimization.
3.1. The Zero-Mile Diet
The most immediate and quantifiable carbon benefit of Infarmight is the drastic reduction in food miles. By placing farms directly in the cities where the food is consumed, the need for long-haul trucking, air freight, and refrigerated shipping is minimized or eliminated.
| Environmental Factor | Conventional Farming | Infarmight Vertical Farming | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Use | High (70% of global freshwater) | Up to 95% less | Water conservation, drought resilience |
| Land Use | Extensive (deforestation risk) | Minimal (urban integration) | Habitat preservation, land sparing |
| Pesticides/Herbicides | High reliance | Zero use | Ecosystem health, no chemical runoff |
| Food Miles | High (long-distance transport) | Near-zero (localized production) | Reduced carbon emissions from transport |
| Yield per Acre | Standard | Up to 400x higher | Increased food security with less land |
This localization not only cuts down on fossil fuel consumption but also ensures that the produce is fresher, leading to the next major environmental benefit: waste reduction.
3.2. Optimizing Energy Use
While vertical farms require energy for lighting and climate control, Infarmight is committed to mitigating this through smart technology and renewable integration.
- LED Technology: They utilize highly efficient LED lighting, tailored to the specific photosynthetic needs of each crop, minimizing wasted energy.
- AI Climate Control: The AI system precisely manages temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels, ensuring optimal conditions with minimal energy fluctuation.
- Renewable Sourcing: Infarmight actively partners with energy providers to source power from renewable energy credits or directly integrates solar and wind power where feasible, moving towards a net-zero operational model.
4. The End of Agrochemicals: A Healthier Planet
The widespread use of synthetic pesticides and herbicides in conventional farming has devastating consequences for the environment. These chemicals poison beneficial insects, including pollinators like bees, disrupt soil health, and contaminate water sources.
Infarmight’s indoor, controlled environment eliminates the need for these harmful substances entirely.
4.1. Pest-Free by Design
The sealed nature of the vertical farm acts as a natural barrier against pests and diseases. This controlled environment means there is no exposure to external threats, making pesticides obsolete. The food grown by Infarmight is inherently chemical-free, which is a massive win for consumer health and, more importantly, for the health of the planet’s biodiversity.
The absence of herbicides also protects soil ecosystems, even though the plants are not grown in soil. The broader environmental impact is the reduction in the global demand for these toxic chemicals, leading to cleaner air, water, and soil across the entire agricultural landscape.
5. Waste Reduction and Food Security
Food waste is a global tragedy with significant environmental costs. Roughly one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally, contributing to landfill emissions and squandering the resources used to produce it. Infarmight’s model addresses waste at multiple points.
5.1. Minimizing Post-Harvest Loss
In traditional supply chains, a significant amount of produce is lost during harvesting, sorting, and long-distance transportation. Infarmight’s hyper-local model drastically reduces this post-harvest loss. The produce is often harvested and delivered to the consumer or retailer within hours, minimizing spoilage and the need for excessive packaging or chemical preservatives.
Furthermore, the precise, year-round growing cycle allows for just-in-time production, aligning supply perfectly with demand. This eliminates the overproduction that often leads to massive waste in seasonal, weather-dependent farming.
5.2. Maximizing Resource Utilization
Infarmight’s commitment to a circular economy extends to its growing medium and nutrient solutions. The systems are designed to be highly durable and reusable. The minimal organic waste generated is often composted or repurposed, ensuring that the entire operation approaches a zero-waste ideal.
6. Resilience and Climate Change Adaptation
Climate change introduces volatility and unpredictability into traditional agriculture. Extreme weather events—droughts, floods, and heatwaves—are becoming more frequent, threatening crop yields and food security. Infarmight’s controlled environment agriculture (CEA) offers a powerful form of climate change adaptation.
6.1. Weather-Proof Production
Infarmight’s farms are entirely insulated from external weather conditions. This means that food production remains stable and predictable, regardless of a heat dome in the summer or a deep freeze in the winter. This resilience is a crucial environmental benefit, as it reduces the pressure to expand farming into marginal or ecologically sensitive lands when traditional harvests fail.
6.2. Localized Food Sovereignty
By enabling food production in any climate, Infarmight empowers communities to achieve greater food sovereignty. This localization reduces reliance on complex, fragile international supply chains, which are themselves major sources of carbon emissions and environmental risk. A resilient, localized food system is an inherently sustainable one.
7. Visualizing the Impact
To truly appreciate the scale of Infarmight’s environmental contribution, it is helpful to visualize the technology and the produce it yields. The following images showcase the precision, density, and freshness that define this new era of farming.
| Image Description | URL |
|---|---|
| Vertical Stacks (Urban Integration) |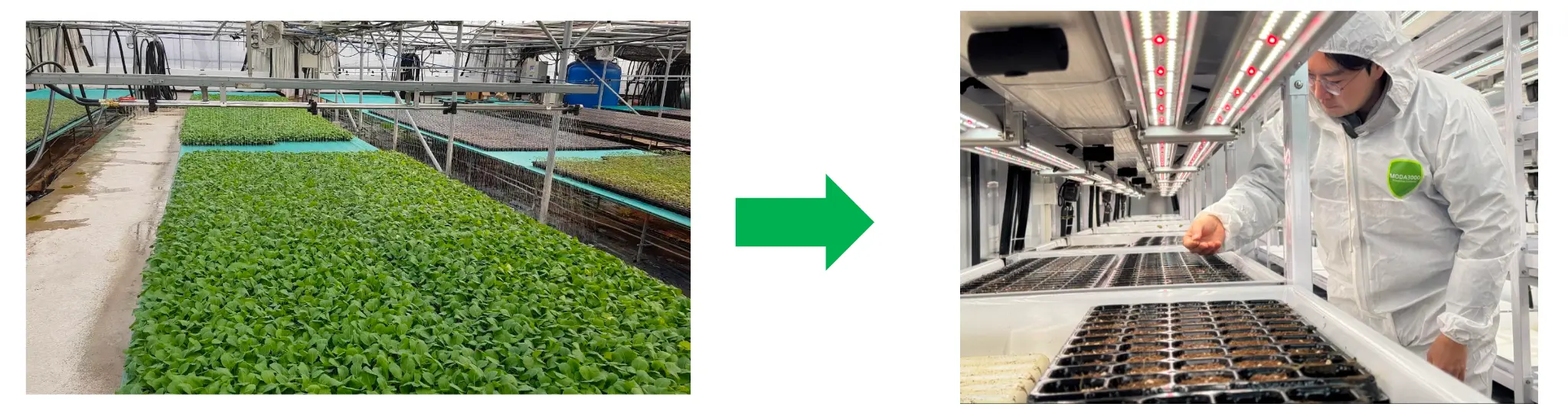  |
| Close-up of Produce (Chemical-Free Growth) |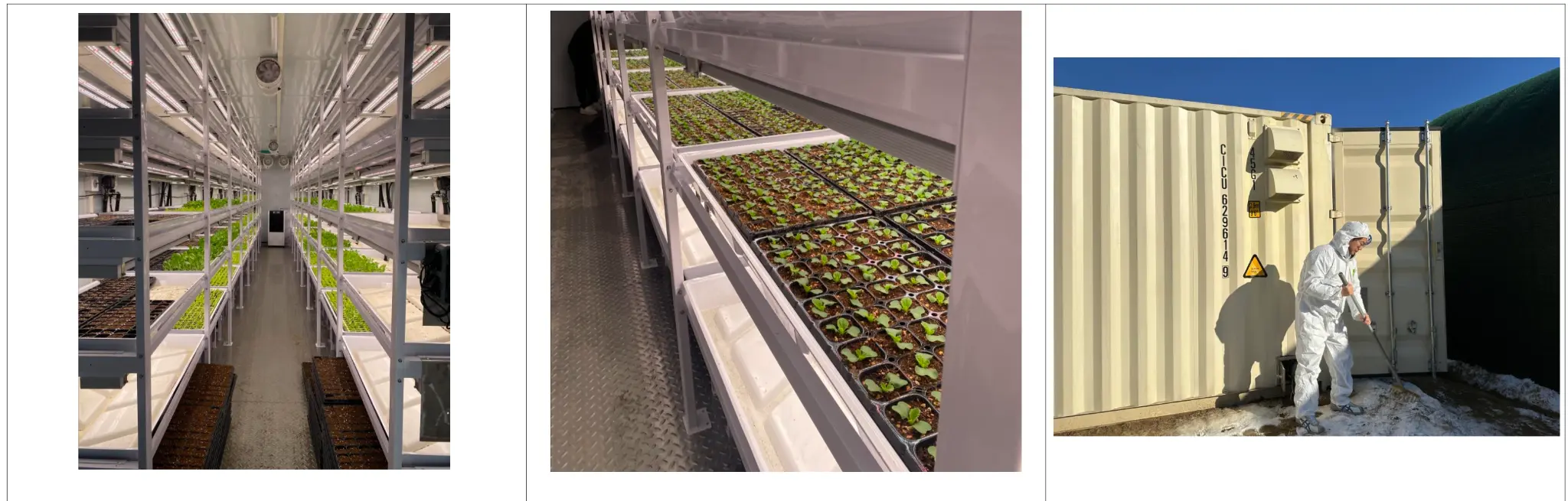  |
| Farming at Scale (Efficiency and Density) |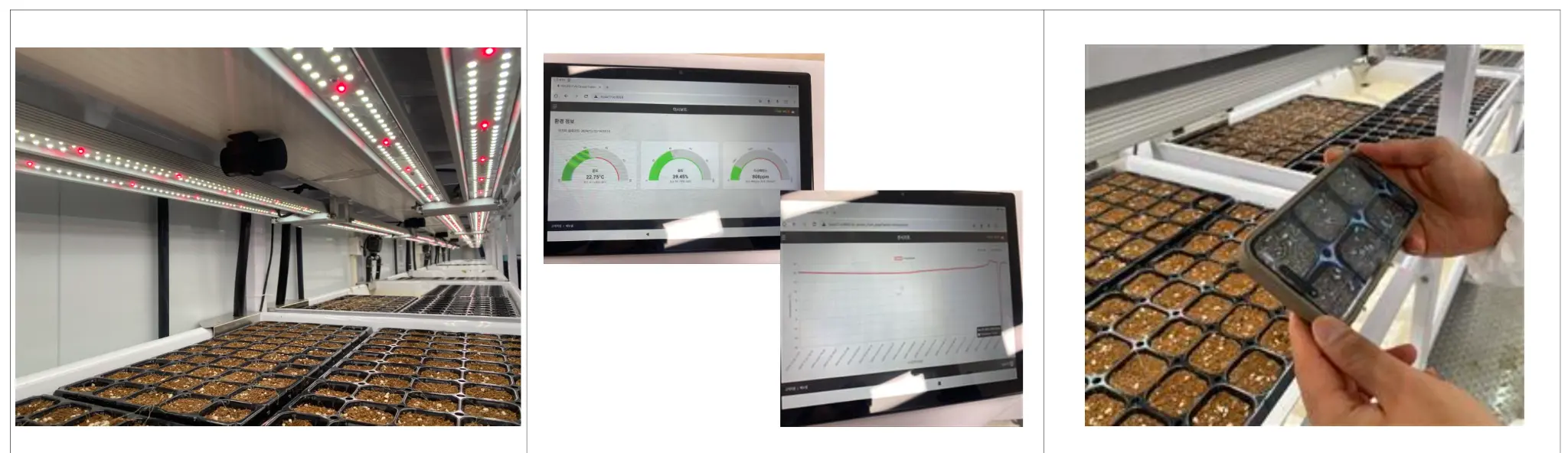  |
| Fresh Harvest (Reduced Waste) |  |
| Leafy Greens (Visual Appeal) |  |
8. The Future is Vertical: Infarmight’s Global Vision
Infarmight is not merely a technology company; it is an environmental movement disguised as a smart farm. Their vision extends beyond the current generation of leafy greens and herbs to a future where staple crops can be grown indoors, further reducing the environmental burden of global agriculture.
The long-term impact of their model is the creation of a decentralized, hyper-efficient, and ecologically restorative food system. By proving that high-quality, high-yield food production can be achieved with minimal water, zero pesticides, and a tiny land footprint, Infarmight provides a blueprint for every nation seeking to meet its food security goals while honoring its climate commitments.
This transition is not without its challenges, particularly concerning the initial energy investment and the scaling of technology. However, as renewable energy sources become cheaper and more accessible, the economic and environmental calculus overwhelmingly favors the Infarmight model. The environmental benefits—from water conservation and land preservation to carbon reduction and biodiversity protection—are too significant to ignore.
Infarmight is cultivating more than just crops; it is cultivating a greener, more resilient tomorrow for all. The smart farm revolution is here, and it promises a sustainable harvest for generations to come.
Leave a Reply